While Loop
Topic Covered in the Lesson
- Know about how to use a while loop in a python program.
- Different types of statements in a while loop.
Key Learning Outcomes
- While loop basics
- Break statements
- Continue statements
- Else statements
Let’s begin!
While Loop Basics
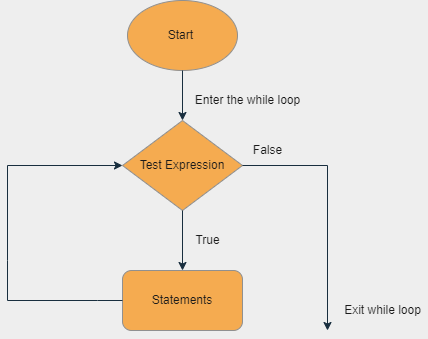
Python While Loop is used to execute a block of statements repeatedly until a given condition is satisfied. And when the condition becomes false, the line immediately after the loop in the program is executed. While loop falls under the category of indefinite iteration.
Indefinite iteration means that the number of times the loop is executed isn’t specified explicitly in advance.
Syntax:
while expression:
statement(s)
Here, Statements representing all the statements indented by the same number of character spaces after a programming construct are considered to be part of a single block of code. Python uses indentation as its method of grouping statements.
When a while loop is executed, expr is first evaluated in a Boolean context and if it is true, the loop body is executed. Then the expr is checked again, if it is still true then the body is executed again and this continues until the expression becomes false.
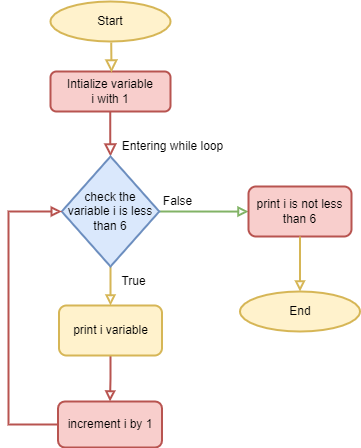
Flowchart of While Loop
With the while loop we can execute a set of statements as long as a condition is true.
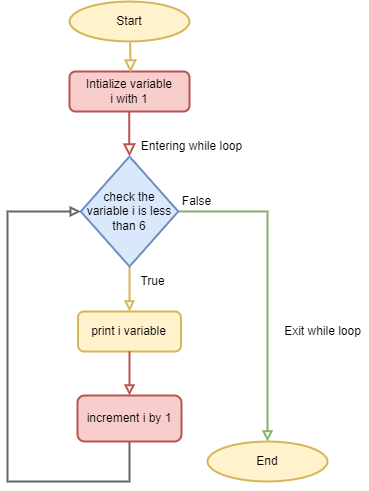
For Example
Print i as long as i is less than 6
Flowchart
i = 1
while i < 6:
print(i)
i += 1
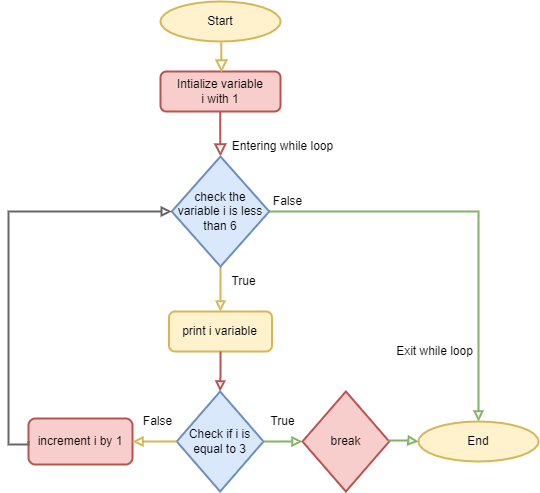
The break statement
i = 1
while i < 6:
print(i)
if i == 3:
break
i += 1
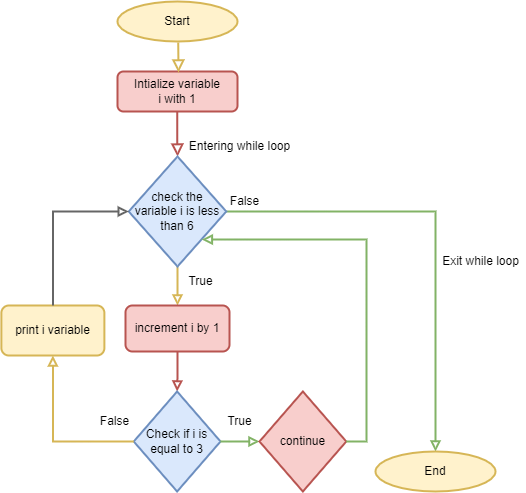
The continue statement
i = 0
while i < 6:
i += 1
if i == 3:
continue
print(i)
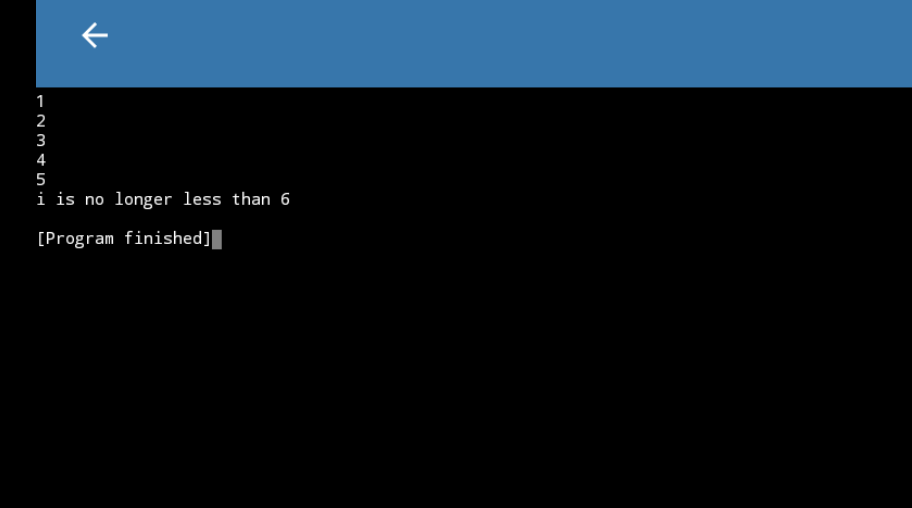
The else statement
i = 1
while i < 6:
print(i)
i += 1
else:
print("i is no longer less than 6")
Activity : Table of a Number
The table consists of multiples of whole numbers from 1 to 20. Mathematics tables from 1 to 20 will help us to solve multiplication problems in a quick way. So let us try to write a simple program for implementing a table of numbers.
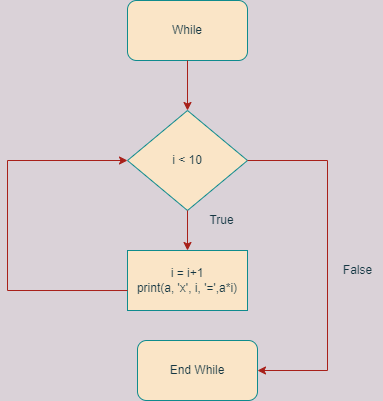
Step 1 – Flowchart
Step 2 – Let’s Code
The code is pretty simple. Let’s get straight to it. Follow the steps below:
- First, ask the user to enter a number. So, we will use the input() function with a print statement.
print("Enter a number: ")
a = input()
- Now we will take the integer type for the age. Here, we will write int() in the variable.
print("Enter a number: ")
a = input()
a = int(a)
- Initialize i is equal to 0 and with the help of a while loop we will make a table as per the user input till i < 10.
print("Enter a number: ")
a = input()
a = int(a)
i = 0
while i < 10
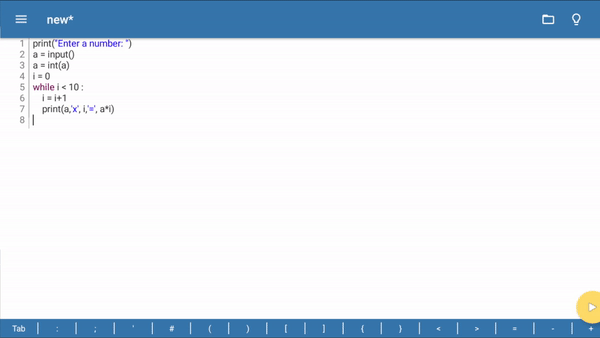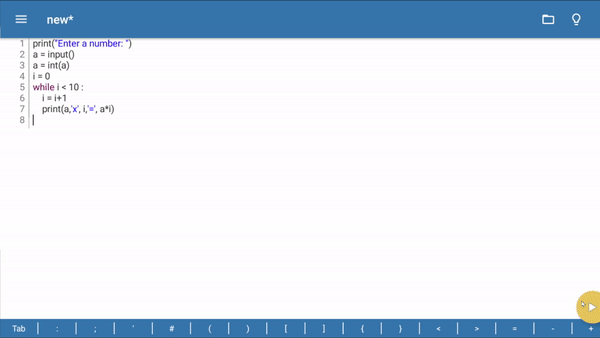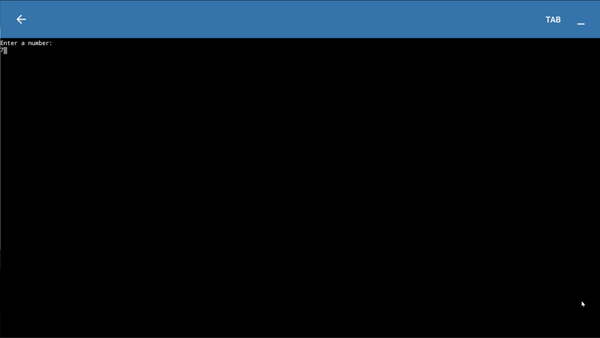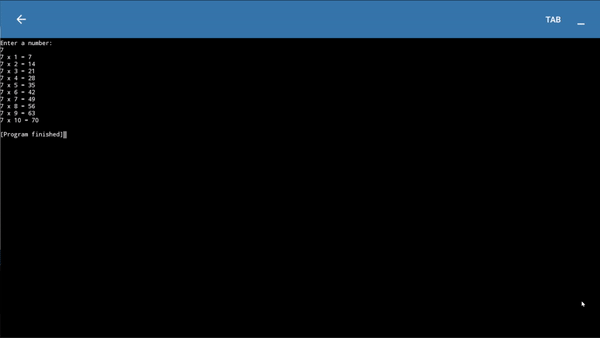
- Now we will increment variable i by 1 and we will print table till variable i becomes 10.
print("Enter a number: ")
a = input()
a = int(a)
i = 0
while i < 10 :
i = i+1
print(a,'x', i,'=', a*i)